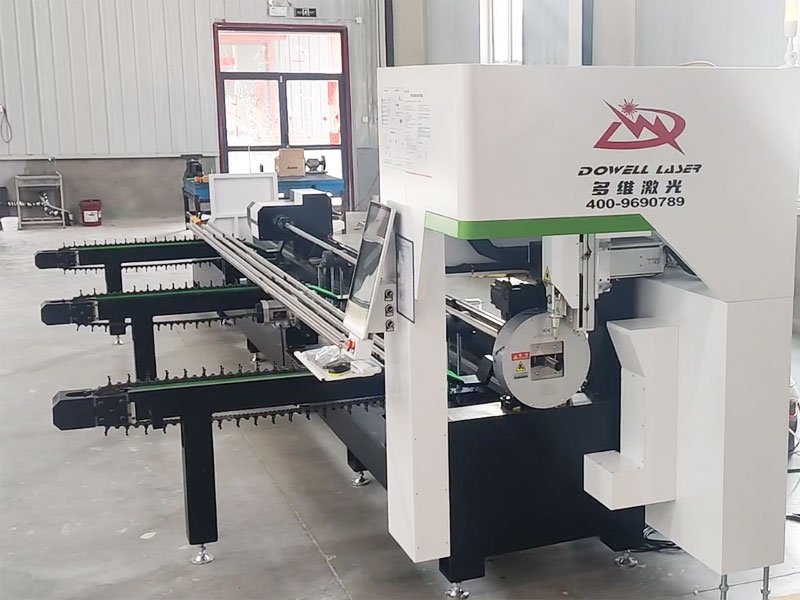
In the world of manufacturing, the need for precision and efficiency is constantly growing. As industries seek innovative ways to improve product quality while reducing costs, laser welding has emerged as a cutting-edge solution. But what exactly is laser welding, and why is it considered a revolutionary method for joining metals?
In this article, we’ll explore the technology behind laser welding, its advantages over traditional methods, and its applications in various industries.

What is Laser Welding?
Laser welding is a modern technique used to join metals using the intense heat generated by a focused laser beam. The process works by directing a concentrated laser onto the joint area of two metal pieces, causing the metal to melt and fuse together. The laser beam is highly focused, allowing for precise and controlled welding with minimal heat distortion.
Laser welding is part of a broader category of laser-based technologies used in manufacturing, offering distinct advantages over traditional welding methods. While conventional welding techniques like MIG (Metal Inert Gas) and TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) involve applying heat through electrical arcs or flames, laser welding utilizes a focused beam of light to achieve the same result—joining metals—without the need for physical contact.
How Does Laser Welding Work?
Laser welding operates on the principle of high-energy density. A laser beam is directed onto the workpiece, and the focused energy melts the material at the joint. As the material cools, it solidifies and forms a strong, durable weld.
Key Steps in the Laser Welding Process:
- Preparation: The metal surfaces to be welded are carefully aligned.
- Laser Application: The laser beam is directed at the joint area, where it melts the material.where it
- Cooling and Solidifying: The melted material quickly cools down and forms a strong weld, with minimal distortion and heat-affected zones.
One of the major benefits of laser welding is its ability to work with a variety of materials, including metals that are difficult to weld using traditional methods, such as aluminum alloys and titanium.

Advantages of Laser Welding
Laser welding has several advantages over traditional welding methods, making it a popular choice in modern manufacturing.
1. Precision and Accuracy
Laser welding offers unparalleled precision. The laser beam is highly focused, allowing for small, narrow welds with very little distortion. This makes it ideal for applications that require tight tolerances and high-quality finishes, such as in the aerospace, automotive, and electronics industries.
2. Speed and Efficiency
Laser welding is a fast process, reducing production time and increasing overall efficiency. This is especially important in industries where high throughput is essential, such as mass production or automated systems.
3. Minimal Heat Affected Zone (HAZ)
One of the key benefits of laser welding is the minimal heat-affected zone. Traditional welding methods often cause a large HAZ, which can weaken the metal or cause unwanted deformation. Laser welding, however, applies heat only to the joint area, minimizing the risk of damage to the surrounding material.
4. Clean and Strong Joints
Laser welding creates strong and clean joints with minimal spatter. The result is a higher-quality weld with fewer defects and less post-welding clean-up.
5. Automation and Flexibility
Laser welding can easily be integrated into automated systems. This is particularly beneficial for industries that require mass production or robotic welding, such as in the automotive industry. The automation of the process improves consistency and reduces the need for manual labor.
Laser Welding vs Traditional Welding:
1. Speed
Laser welding is significantly faster than MIG or TIG welding, especially when used in automated systems. This makes it an ideal choice for industries with high-volume production needs.
2. Precision
Laser welding provides a higher degree of precision, making it perfect for applications that require tight tolerances and high-quality welds. Traditional welding methods, while effective, can be less accurate, leading to potential issues like warping or porosity.
3. Heat Affected Zone (HAZ)
Laser welding produces a much smaller heat-affected zone compared to traditional welding methods. This reduces the risk of material distortion and degradation of the surrounding metal, which is particularly important in sensitive materials like stainless steel and titanium.
4. Material Compatibility
Laser welding is highly effective for welding materials that are difficult to weld using traditional methods. For instance, it is especially useful for thin sheets of metals like aluminum, copper, and titanium, which are often challenging for MIG and TIG welders to handle.
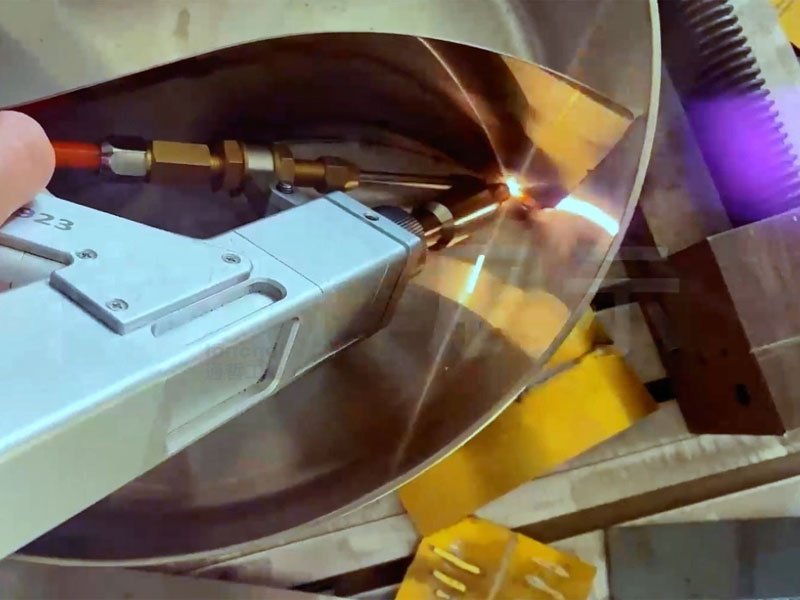
Applications of Laser Welding
1. Automotive Industry
In the automotive industry, laser welding is used for joining body panels, exhaust systems, and battery components. The precision and speed of laser welding help manufacturers meet high-quality standards while reducing production costs.manufacturers meet high-quality standards while reducing production
2. Aerospace
In aerospace, where material integrity is critical, laser welding is used to join lightweight alloys and high-strength metals. The minimal heat affected zone ensures that the structural properties of the materials remain intact.
3. Electronics and Electrical Components
Laser welding is increasingly being used in the production of electrical connectors, microchips, and other small, delicate parts. The accuracy and low thermal input of laser welding make it ideal for these applications.
4. Medical Devices
Laser welding is also used in the medical device industry to join surgical instruments, implantable devices, and medical tubing. The precision and minimal risk of contamination make it an excellent choice for these high-stakes applications.
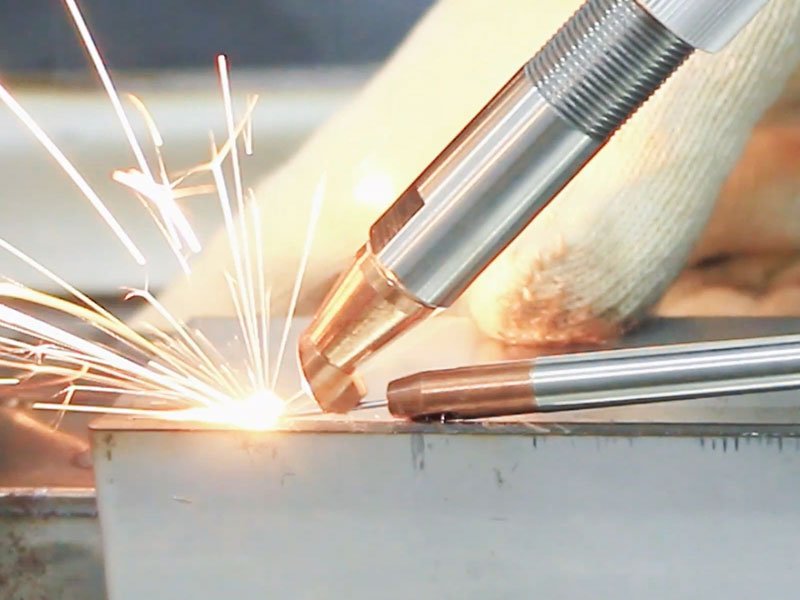

Conclusion
Laser welding is undoubtedly one of the most innovative technologies in modern manufacturing. With its speed, precision, and versatility, it is quickly becoming the preferred method for joining metals in a variety of industries. As the technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more applications and improvements in laser welding’s efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Whether you’re a manufacturer looking to improve your production processes, or a researcher interested in new welding technologies, laser welding represents a cutting-edge solution that offers significant advantages over traditional methods.
FAQs:
1. What is laser welding?
Laser welding is a technique that uses a high-energy laser beam to join two pieces of metal by melting and fusing them together.
2. What are the advantages of laser welding over traditional methods?
Laser welding is faster, more precise, and produces a smaller heat-affected zone compared to traditional methods like MIG or TIG welding.
3. Can laser welding be used for all types of metals?
Yes, laser welding can be used for a variety of metals, including aluminum, stainless steel, titanium, and even difficult-to-weld materials like copper.
4. What industries use laser welding?
Laser welding is widely used in the automotive, aerospace, electronics, and medical industries, among others.



