Servo motor is an important part of laser cutting equipment. It can provide stable power supply to achieve stable work. Many people do not know much about servo motors. This article will help you understand the stepper motor servo motor difference.

Servo motors vs stepper motors difference
What is a servo motor?
The function of the servo motor is to control the speed uniformly and stably with the change of voltage, and to locate by pulse. When receiving a pulse current, it will rotate the corresponding angle of a pulse to achieve uniqueness.
What is a stepper motor?
A stepper motor is a motor that converts electrical pulse signals into corresponding angular displacement or linear displacement.
How do servo motors /stepper motor work
The servo motor itself has the function of emitting pulse current, rotating an angle will produce a corresponding number of pulses, and the servo motor receives the pulse to form a response, so that the system knows how many pulses are sent to the servo motor and how many pulses are recovered, thus accurately controlling the rotation of the motor.
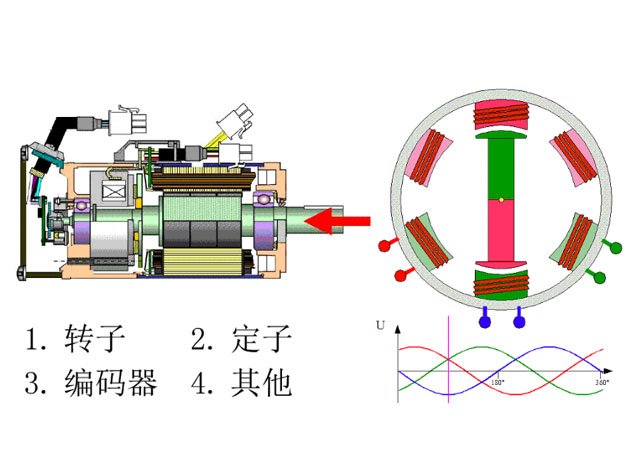
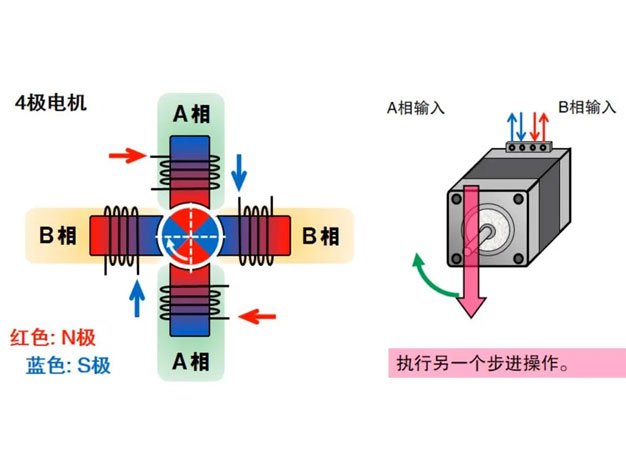
Every time a pulse signal is input to the stepper motor, the rotor rotates a set angle or advances a certain distance. Therefore, the output angular displacement or linear displacement of the stepper motor is proportional to the number of input pulses, while the rotational speed is proportional to the pulse frequency. This means that the angular displacement can be controlled by controlling the number of pulses to achieve accurate positioning; by controlling the pulse frequency, the rotation speed and acceleration of the motor can be controlled to achieve speed regulation.
Difference between servo motor and stepper
Working principle
A stepper motor is an open-loop control element stepper motor device that converts electrical pulse signals into angular displacement or linear displacement. Check out the working principle of a stepper motor.
The servo motor relies on pulses to position and has the function of sending pulses
Cost
Stepper motors have advantages in terms of cost performance. To achieve the same function, the price of a servo motor is higher than that of a stepper motor with the same power;
The advantages of high response, high speed and high precision of servo motors determine the high price of the product, which is inevitable.
Anti-resonance
The stepper system has an inherent resonance point. The SR series stepper driver automatically calculates the resonance point and uses it to adjust the control algorithm to achieve the purpose of suppressing resonance. It greatly improves the stability of the intermediate frequency and enables greater stability at high speeds. Torque output, better high-speed performance.
The servo motor runs smoothly and does not vibrate at low speeds. The AC servo system has a resonance suppression function that can make up for the lack of mechanical rigidity. The system also has a frequency analysis function (FFT) inside the system that can detect the resonance point of the machine to facilitate system adjustment.
Running performance
Stepper motors are generally open-loop controlled. motor;
The servo motor adopts closed-loop control, which is easier to control and there is no out-of-step phenomenon.
Speed and overload capacity
Stepper motors are prone to low-frequency vibration
This phenomenon does not occur with servo motors. Its closed-loop control characteristics determine its excellent performance during high-speed operation.

Technical difference stepper vs servo motor
1. Control method
- Stepper motors use open-loop control, relying on pulse signals to control the motor rotation angle, and do not have position feedback.
- Servo motors use closed-loop control, relying on encoders to detect the motor rotation angle and compare it with the target position to correct errors and ensure control accuracy.
2. Accuracy
- Due to open-loop control, stepper motors have step errors and cumulative errors, and the accuracy is lower.
- Due to closed-loop control, servo motors can overcome the errors of stepper motors, and the accuracy is higher.
3. Speed
- Stepper motors are prone to resonance when running at low speeds, and their high-speed performance is poor.
- Servo motors can overcome the resonance problem, and the high-speed performance is better.
4. Torque
- The output torque of a stepper motor decreases as the speed increases. The low-speed torque is larger, and the high-speed torque is smaller.
- The output torque of a servo motor is basically constant within the rated speed range, and it can provide a larger torque.
5. Response speed
- The response speed of a stepper motor is slower, and the acceleration is limited.
- The response speed of a servo motor is faster, and the acceleration is greater.
6. Load capacity
- Stepper motors do not have overload capacity, and they are prone to lose steps or stall when overloaded.
- Servo motors have overload capacity and can withstand a certain amount of overload.
7. Noise and vibration
- Stepper motors are prone to noise and vibration when running at low speeds.
- Servo motors can effectively suppress noise and vibration.
8. Cost
- Stepper motors have a simple structure and are relatively low in cost.
- Servo motors have a complex structure and are relatively high in cost.
9. Application scenarios
- Stepper motors are suitable for occasions with low requirements for accuracy and speed, such as position control and speed control.
- Servo motors are suitable for occasions with high requirements for accuracy, speed, and load, such as CNC machine tools, robots, and new energy vehicles.
Difference servo stepper
Servo motor or stepper motor are two commonly used motor types. They have different working principles and performance characteristics. Choosing the right motor requires comprehensive consideration based on application requirements.

Applications of stepper motors and servo motors
Stepper motors and servo motors are two commonly used motor types. They have different working principles and performance characteristics, so there are also differences in their application fields.
Application for stepper motor :
- CNC machine tools: used to control the feed movement of machine tools to achieve precise positioning.
- Automation equipment: used to control the feeding, sorting, cutting, and other actions of the automated production line.
- 3D printer: used to control the XYZ axis movement of the printer to achieve precise printing.
- Robot: Used to control the joint movement of the robot to achieve flexible movements.
- Instrumentation: used to control the rotation of the instrument pointer to achieve indication and measurement.
- Home appliances: Used to control certain functions of home appliances such as washing machines, air conditioners, and rice cookers.
Servo motor applications
- Industrial control: used to control industrial equipment such as mechanical arms, robots, and automated production lines.
- CNC machine tools: used to control the speed and torque of the machine tool spindle to achieve high-precision machining.
- New energy vehicles: used to control the motor speed and torque of electric vehicles to achieve efficient driving.
- Aerospace: Used to control rudder surfaces, flaps, and other components of aircraft, missiles and other aircraft.
- Medical equipment controls precision instruments such as surgical robots and medical imaging equipment.
- Robot: Used to control the joint motion of the robot to achieve high-precision movements.
Comparison of applications between stepper motor or servo
- Stepper motors have the advantages of simple structure, low cost, and convenient control, but their accuracy and speed are relatively low.
- Servo motors have the advantages of high precision, fast speed, and sensitive response, but their structures are complex and their costs are high.
- Therefore, when selecting a motor type, factors such as application needs, cost, and technical requirements need to be considered.

How to select servo motor or stepper motor
- If the application does not have high requirements for accuracy, speed, and torque, and the cost budget is limited, you can choose a stepper motor.
- If the application requires high accuracy, speed, and torque, you can choose a servo motor.
- If the application requires complex motion control, servo motors can be selected.
- If the application requires working in harsh environments, you need to choose a motor with a protection rating.
How to Choose a Stepper Motor
1. Determine the motor size
- Consider the installation space and motor power requirements.
- The motor size is usually determined by the motor’s outer diameter and length.
- Common stepper motor sizes: NEMA17, NEMA23, NEMA34, NEMA42, etc.
2. Determine the motor torque
- Consider the load torque, acceleration requirements, and working environment.
- Motor torque is usually expressed in Nm or lb-in.
- Stepper motor torque can be increased by selecting a different motor model or adding a reducer.
3. Determine the motor speed
- Consider the application requirements and the motor’s rated speed.
- Motor speed is usually expressed in RPM.
- The speed of a stepper motor can be adjusted by changing the pulse frequency of the driver.
4. Determine the motor accuracy
- Consider the application requirements and the motor’s step angle.
- Motor accuracy is usually expressed in step angle or number of pulses per revolution.
- The accuracy of a stepper motor can be improved by using microstepping technology.
5. Select a motor driver
- Select a driver that matches the motor.
- The driver is mainly used to control the motor movement.
- Common driver types: pulse/direction driver, servo driver, etc.
6. Other factors
- Consider motor price, noise, vibration, etc.
- Choose a motor that meets the application requirements and budget.
How to Choose a Servo Motor
1. Determine the motor size
- Consider the installation space and motor power requirements.
- The motor size is usually determined by the motor’s outer diameter and length.
- Common servo motor sizes: 40mm, 60mm, 80mm, 110mm, etc.
2. Determine the motor torque
- Consider the load torque, acceleration requirements, and working environment.
- Motor torque is usually expressed in Nm or lb-in.
- Servo motor torque can be increased by selecting a different motor model or adding a reducer.
3. Determine the motor speed
- Consider the application requirements and the motor’s rated speed.
- Motor speed is usually expressed in RPM.
- The speed of a servo motor can be adjusted by changing the command frequency of the driver.
4. Determine the motor accuracy
- Consider the application requirements and the motor encoder resolution.
- Motor accuracy is usually expressed in pulses per revolution (PPR).
- The accuracy of a servo motor can be improved by selecting an encoder with a higher resolution.
5. Select a motor driver
- Select a driver that matches the motor.
- The driver is mainly used to control the motor movement.
- Common driver types: AC servo driver, DC servo driver, etc.
6. Select a motor controller
- Select a controller that matches the driver.
- The controller is mainly used to send control commands to the driver.
- Common controller types: PLC, motion control card, PC, etc.
7. Other factors
- Consider motor price, noise, vibration, protection level, etc.
- Choose a motor that meets the application requirements and budget.
Difference between servo and stepper factor
| Factor | Stepper Motor | Servo Motor |
|---|---|---|
| Price | Lower | Higher |
| Accuracy | Lower | Higher |
| Speed | Lower | Higher |
| Torque | Lower | Higher |

Fiber laser cutting machine servo motor function
Mechanical factors
Mainly reflected in the design, transmission method, installation, material, mechanical wear and other aspects.
Mechanical internal stress, external force and other factors
Due to differences in mechanical materials and installation, the mechanical internal stress and static friction of each transmission shaft on the equipment will be inconsistent. If one of the two axes participating in trajectory interpolation control has greater internal stress or static friction, it will consume the servo torque to a certain extent, causing the acceleration of this axis to slow down, resulting in deformation of the machining contour. The internal stress problem of the drive shaft can be observed through the waveform curve generated by the servo drive feedback.
External force acting on the shaft. In general plate cutting machines, there is no contact between each axis and the workpiece, and the external force that may be received is limited. For pipe cutting machines, the pipe feeding axis will participate in interpolation during cutting, while the other axis is generally non-contact. Due to the influence of the clamp, the pipe will produce a reverse force on the pipe feeding axis. The force conditions of the two axes participating in the interpolation control are inconsistent, and the cutting effect will definitely be affected.
Mechanical resonance
The greater impact of mechanical resonance problems on servo is that it cannot continue to improve the responsiveness of the servo motor, causing the overall equipment to run in a relatively low response state.
CNC system factors
The debugging effect of the servo is not obvious, and the control system needs to be adjusted. When processing fiber laser cutting machines, the linear speed is usually relatively constant, and the speed is the same on both straight lines and curves.
Mechanical jitter
Mechanical jitter is essentially a problem of the natural frequency of the machine. It usually occurs in single-end fixed cantilever structures, especially during the acceleration and deceleration stages. Low-frequency jitter will have a large wave-like shape in the workpiece, and higher-frequency jitter will have a jagged shape.
The role of the servo motor is still very important and we must not ignore it. Therefore, it is still recommended that everyone choose a guaranteed merchant when purchasing fiber laser cutting!
There are big difference between a stepper motor and a servo motor in terms of working principle, overload capacity, operating performance and cost. However, both have their own advantages. If users want to choose between them, they need to combine their actual needs and application scenarios.



