Many customers do not understand the working principle of the fiber laser cutting machine before buying it. This is very troublesome for choosing the appropriate cutting equipment.
The laser cutting equipment is a new type of industrial sheet metal cutting machine. Its current application range is relatively small. Widely used in different laser cutting applications in sheet metal, glass, wood, foam, cardboard, etc., it can not only cut, but also perform engraving and marking functions.
Continue with the article below to start learning more about specifically what does a laser cutter do.
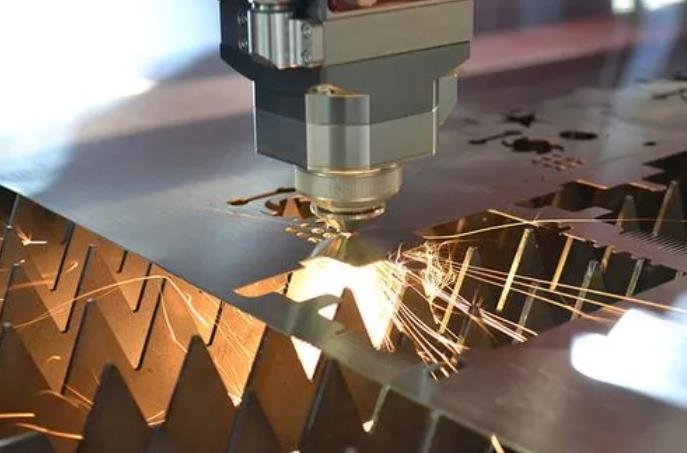
Fiber laser cutting machine working principle
The method of separating metal materials by the heat energy of the gas flame is called gas flame gas cutting, or gas cutting for short. The main target of gas cutting is general structural steel, which is a blanking method used in the preparation process of production.
The gas cutting of fiber metal laser cutting machine is widely used in various industries such as metallurgy, machinery, electric power, petrochemical industry, boilers, and pressure vessels, vehicles, shipbuilding, and so on.
What does a laser cutter do
A simple understanding of laser cutting is CNC technology used to cut sheet metal. However, this equipment can produce high-energy heat. It is a CNC equipment with relatively high precision. Technical training is required during operation.
What is oxy-fuel cutting
Cutting refers to cnc oxy fuel cutting machine, also called oxygen flame cutting. It uses the heat generated by combustible gas (ethane, propane, liquefied petroleum gas, natural gas, etc.) and oxygen combustion (flame) to heat the surface of the workpiece to a certain temperature (the temperature is higher than the melting point), and the cutting oxygen sprayed to high purity and high flow speed will burn the surface of the workpiece to generate slag and release a lot of heat.
The heat released by the combustion of the workpiece, the high-temperature slag, and the heat generated by the gas flame continue to heat the lower layer of the bow and arrow and the leading edge of the incision to reach the ignition point (combustion temperature built-in oxygen, called the ignition point of the workpiece) until the bow bottom. At the same time, the cutting oxygen stream blows away the slag, thereby forming a cut to cut and separate the workpiece.
Related articles:
- Comprehensive Best Laser Cutting Materials List
- How Deep Can A Laser Cutter Cut & Laser Cutting Depth Influencing Factors
- Ultimate Guide : How Thick Can A Laser Cutter Cut Steel

Laser cutting working principle influencing factors:
A laser generator produces a laser beam:
The laser generator in the laser cutting machine produces a high-energy, highly concentrated laser beam. Commonly used laser types include CO2 laser, fiber laser and solid laser.
Laser beam guidance and focusing:
Through optics, the laser beam is directed and focused into a small diameter spot. Lenses or mirrors are often used to control the path of the laser beam and focus it to a smaller spot.
Material absorbs laser energy:
When a laser beam strikes a material surface, the material absorbs the laser energy. The absorption rate will vary between different materials, and some metal materials have higher absorption rates for lasers.
Materials are heated to melt or vaporize:
The high energy density of the laser causes the material to rapidly heat up to a temperature where it melts or vaporizes. A large amount of heat energy is consumed to melt or vaporize the material to achieve cutting.
Auxiliary gas injection:
During the cutting process, auxiliary gas (such as nitrogen, oxygen or inert gas) is often injected through a nozzle to protect the laser cutting area, blow away the melted material and help speed up the cutting.
Motion Control System:
Laser cutting machines are usually equipped with a motion control system to control the movement path of the laser cutting head on the material surface. This enables cutting of various complex shapes, controlled by a computer program.

Which gas is best for laser cutting
| Material | Recommended Gas | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | Oxygen (O2) | – Positive focus cutting results in bright or frosted surfaces. |
| surfaces. | ||
| – Negative focus cutting is suitable for high-power | ||
| equipment. | ||
| – Thicker plates: use nitrogen or air for efficiency, | ||
| but thicker materials may have more burrs. | ||
| Stainless Steel | Nitrogen (N2) orAir | – Nitrogen cutting results in a silver-white section. |
| – Air cutting yields a yellow-black section due to | ||
| oxygen’s combustion aiding effect. | ||
| Aluminum Alloy | Nitrogen (N2) orAir | – Both gases produce a silver-white section. |
| – Nitrogen prevents oxidation, while air is faster. | ||
| Zinc-Coated | Nitrogen (N2) or | – Similar cutting principles as stainless steel. |
| Steel | Air | |
| Brass | Nitrogen (N2) or | – Cutting principles similar to stainless steel. |
| Air | ||
| Copper | High-pressure | – Copper, a highly reflective material, uses high |
| Oxygen (O2) | pressure oxygen cutting to reduce laser reflection. | |
| Titanium Alloy | Air or Inert Gas | – Economical choice is air, but inert gases like |
| (Argon for color | argon can be used to maintain original color. | |
| preservation) | ||
| Composite Plate | Air | – Similar cutting principles as stainless steel. |
| – Usually cut with the carbon steel side facing up. | ||
| Special Metals | Air or High- | – For hard special metals, attempt air cutting. If |
| Pressure Oxygen | ineffective, try high-pressure oxygen. | |
| (for difficult | – If all else fails, resort to traditional methods. | |
| materials) |
Related articles:
- Fiber Laser Cutting Problems And Solutions
- Interpreting The Fiber Laser Cutting Speed Chart And Thickness Chart
Application field of fiber metal laser cutting machine
The entire cutting process of fiber metal laser cutting machine can be divided into four interrelated stages:
- The metal surface at the starting point is heated to the ignition point by the preheating flame, and a combustion reaction occurs.
- The lower metal burns.
- The cutting oxygen stream blows away the solution produced by combustion and cuts the metal along the thickness direction.
- Combustion reaction heat and preheating flame heat the upper metal layer on the front edge of the incision to the ignition point and burn.
These four stages are repeated continuously to complete the gas cutting of the work.

According to the different combustible gas used, gas cutting can be divided into oxygen-acetylene gas cutting, oxygen-propane gas cutting, oxygen-liquefied petroleum gas cutting, oxygen-natural gas cutting, and oxygen-hydrogen gas cutting.



